What is a solar charge controller?
A solar charge controller is a device that is responsible for transferring energy from solar panels to batteries to charge them. Its primary function is to protect the batteries from excessive energy or voltage by preventing overcharging. Additionally, it regulates the rate and amount of charge for the batteries.
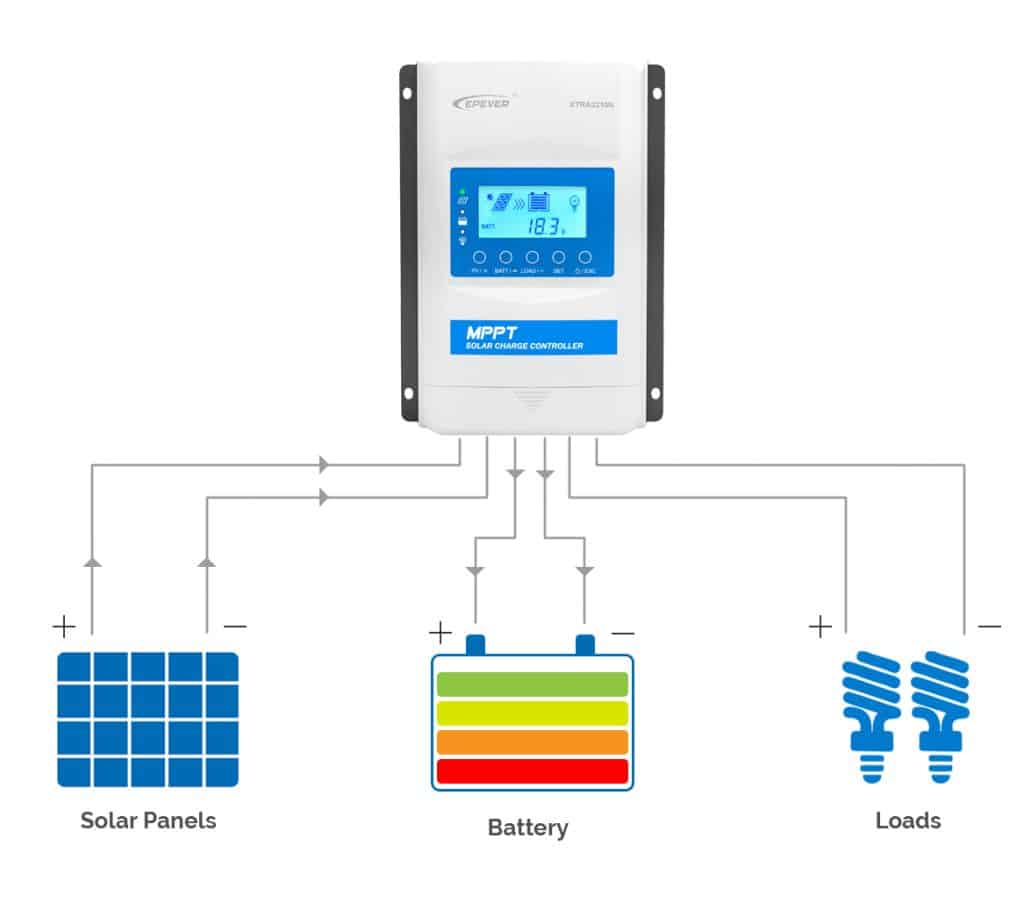
A charge controller in an off-grid solar system also prevents reverse current from batteries to solar panels during overnight or cloudy days. Depending on its type, it can improve system efficiency and optimize power harvest from solar panels. Furthermore, a charge controller typically includes monitoring features that allow system parameters such as current, voltage, and energy to be monitored.

Ultimately, the charge controller serves to increase battery lifespan and optimize the off-grid system.
Why do we need a solar charge controller?
The reason for requiring a solar charge controller is to safeguard and extend the life of batteries.
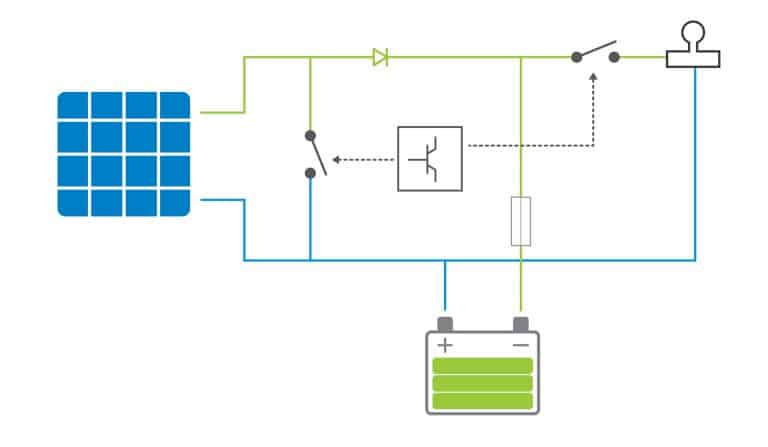
Overcharge protection:
One of the primary protective functions of a charge controller is preventing overcharging, which can harm batteries. The charge controller acts as an intelligent protector by stopping battery charging when the voltage level reaches a certain threshold during the charging process.
Overload / Over current protection:
The solar charge controller also provides overload and overcurrent protection. When running DC loads directly from the charge controller, it monitors the current demand and stops it if it exceeds a certain limit to prevent battery damage. During charging, if the current flowing into the batteries is too high for the circuit to handle, an over-current event may occur, which can cause overheating or fires. The charge controller can adjust the current flow to the batteries and hard limit it if necessary to prevent this from happening.
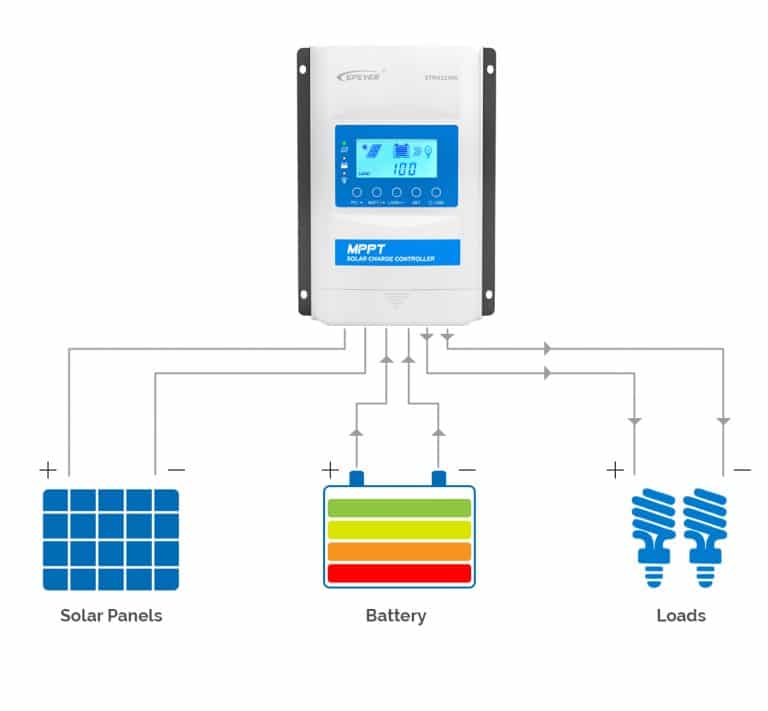
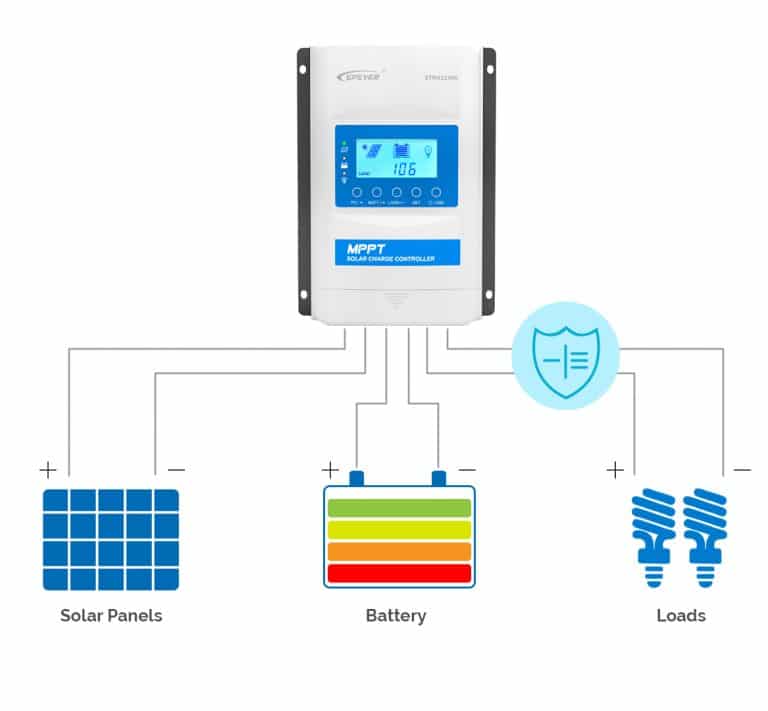
Over-discharge protection
To prevent the battery from being drained completely, a charge controller provides over-discharge protection. When the battery’s state of charge (SOC) drops below a certain level, the charge controller disconnects the loads to manage the amount of discharge. This protective function safeguards the battery, limits the depth of discharge (DOD), and extends the battery’s lifespan.
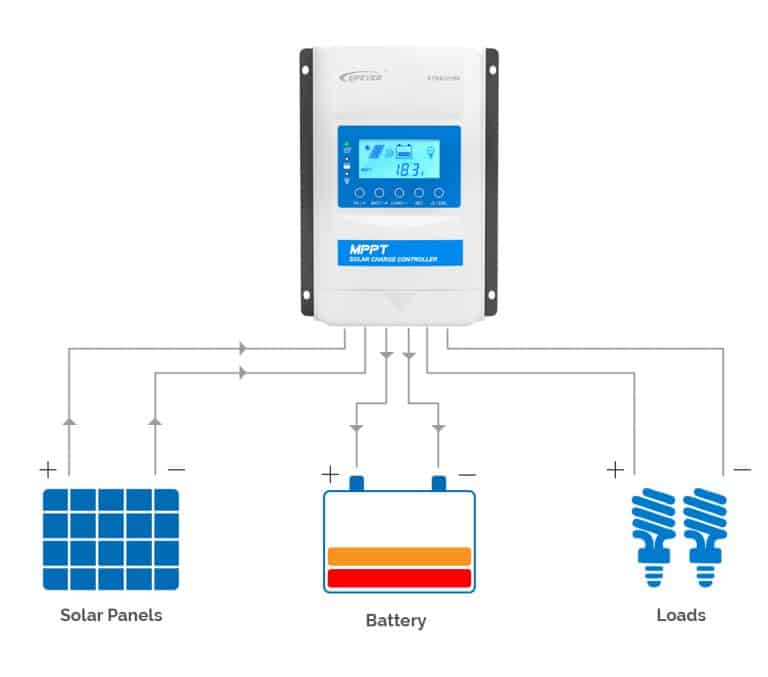

Monitoring system parameters
To monitor the performance of a solar power system, a charge controller can provide information on various parameters such as the voltage of batteries, PV modules, charging current, energy consumption, and production. This data can be displayed through a variety of methods including LEDs, LCDs, remote monitoring devices, and cloud interfaces.

How to choose a solar charge controller?
When it comes to selecting a solar charge controller, it’s important to consider the different types available. The two main categories are pulse width modulation (PWM) and maximum power point tracking (MPPT) charge controllers. While PWM controllers are cheaper, they are less efficient and best suited for smaller systems where efficiency is not a top priority. In contrast, MPPT controllers are more efficient and safer, making them the recommended choice for larger and more complex systems.
MPPT charge controllers can track the maximum power point of the solar panels and obtain the maximum solar energy possible. They can generate up to 30% more power compared to PWM charge controllers and perform better in cloudy conditions with lower solar irradiance. On the other hand, PWM charge controllers act as a valve that regulates the charging current based on the voltage of the batteries.
To choose the right charge controller for your solar power system, consider the size and complexity of your system, the expected solar irradiance, and the efficiency you require. It’s recommended to opt for an MPPT charge controller for larger and more complex systems. However, if you have a smaller system and efficiency is not your top priority, then a PWM controller can be a suitable choice. For more detailed information about the differences between PWM and MPPT charge controllers, we have a comprehensive article that you can refer to.
Compatibility with Lithium batteries
It’s important to note that not all charge controllers are compatible with lithium-ion batteries. These batteries have unique charging and discharge profiles, requiring a multi-stage customized charging and discharge configuration that may not be supported by some charge controllers. It’s crucial to choose a charge controller that is specifically designed to work with lithium batteries to ensure their longevity and performance.
What features you can expect from an MPPT charge controller?
In general, a high-quality MPPT controller that has been well-designed and manufactured will offer the following characteristics
• High MPPT tracking efficiency above 99.5%
• High maximum charge conversion efficiency of as high as 98%
• Support for both lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries
• Programmable
• Multiple load work modes
• Various protective functions
• Temperature derating/protection
• Real-time energy statistics function
• Local, remote, and cloud monitoring
Types and applications
| Type | Supported type of the battery | |
| Lead-acid | Lithium/lead-acid | |
| MPPT | ||
Tracer AN Series (10-40A)MPPT Charge Controller | ||
Tracer AN Series (50-100A) MPPT Charge Controller | ||
DuoRacer Series(10~30A) Dual Battery MPPT Charge Controller | ||
MSC-N Series(20~40A) MPPT Charge Controller | ||
| Tracer BP Series(10~30A) IOT MPPT Charge Controller | ||
| Tracer LPLI Series(10~20A) MPPT Solar Controller & LED Driver | ||
| Tracer BPL Series(10~20A) IOT MPPT Solar Controller & LED Driver | ||
| PWM | EPIPDB-COM Series (10/20A) Dual Battery PWM Charge Controller | LS-LPLW Series(10/20A) PWM Charge Controller & LED Driver LS-LPLI Series(10/20A ) PWM Charge Controller & LED Driver |
| GoMate Series (30A) Flush Mount Charge Controller | ||
| LS-EPD Series (10/20A) PWM Charge Controller | ||
| LS-E(EU) Series(5A~30A) PWM Charge Controller | ||
| LS-B Series(10~30A) PWM Charge Controller | ||
| VS-AU Series(10~60A) PWM Charge Controller | ||
| VS-BN Series(10~60A) PWM Charge Controller | ||
| Camping | High-power solar system | Monitoring system | Off-grid solar home system | Solar light controller | Solar RVs/boats |
XTRA Series(10-40A) MPPT Charge Controller | Tracer AN Series (50-100A) MPPT Charge Controller | XTRA Series (10-40A)MPPT Charge Controller | XTRA Series (10-40A)MPPT Charge Controller | Tracer BP Series (10-30A)IOT MPPT Charge Controller | XTRA Series(10-40A) MPPT Charge Controller |
Tracer AN Series (10-40A)MPPT Charge Controller | iTracer-ND Series (60A) MPPT Charge Controller | Tracer AN Series (10-40A) MPPT Charge Controller | Tracer AN Series (10-40A) MPPT Charge Controller | Tracer LPLI Series(10~20A) MPPT Solar Controller & LED Driver | Tracer AN Series (10-40A)MPPT Charge Controller |
Tracer BP Series (10-30A)IOT MPPT Charge Controller | MSC-N Series (20-40A) MPPT Charge Controller | Tracer AN Series (50-100A) MPPT Charge Controller | Tracer BPL Series(10~20A) IOT MPPT Solar Controller & LED Driver | DuoRacer Series(10~30A) Dual Battery MPPT Charge Controller | |
LS-E(EU)Series (5-30A)PWM Charge Controller | Tracer BP Series (10-30A) IOT MPPT Charge Controller | iTracer-ND Series(60A) MPPT Charge Controller | LS-EPD Series(10/20A) PWM Charge Controller | Tracer BP Series(10~30A) IOT MPPT Charge Controller | |
LS-B Series (10-30A) PWM Charge Controller | LS-B Series (10-30A) PWM Charge Controller | LS-E(EU)Series (5A-30A)PWM Charge Controller | LS-LPLI Series(10/20A ) PWM Charge Controller & LED Driver | VS-AU Series(10~60A) PWM Charge Controller | |
VS-AU Series (10-60A)PWM Charge Controller | VS-BN Series (10-60A) PWM Charge Controller | LS-B Series (10-30A)PWM Charge Controller | LS-LPLW Series(10/20A) PWM Charge Controller & LED Driver | VS-BN Series(10~60A) PWM Charge Controller | |
LS-EPD Series (10/20A)PWM Charge Controller | VS-AU Series (10-60A)PWM Charge Controller | EPIPDB-COM Series(10/20A) Dual Battery PWM Charge Controller | |||
| VS-BN Series (10-60A)PWM Charge Controller | GoMate Series(30A) Flush Mount Charge Controller |
FAQ
Is the MPPT charge controller always better?
MPPT charge controllers are generally more efficient than PWM charge controllers, especially when the solar panel voltage is much higher than the battery voltage. However, the choice of controller depends on the specific system requirements and operating conditions. For small systems with low power requirements, PWM controllers may be more cost-effective.
What happens if you don’t have a charge controller?
Without a charge controller, the battery in a solar power system may not charge correctly, leading to potential damage or even hazards like gas leaks or battery fires.
What’s The Difference Between MPPT and PMW Charge Controllers?
What’s the difference between MPPT and PWM charge controllers?
MPPT charge controllers use algorithms to optimize the solar panel output by tracking its maximum power point, resulting in higher efficiency and power output. PWM charge controllers regulate the voltage output by turning the current flow on and off, leading to power loss due to voltage drop. MPPT controllers are more efficient and suitable for higher voltage solar panels, while PWM controllers are cheaper and better for smaller systems with lower power requirements. For further information, please refer to this comprehensive article.
