Understanding Solar Inverters: On-Grid, Off-Grid & Hybrid
- 31 March 2025
- 25 views
- No Comments
Understanding Solar Inverters: On-Grid, Off-Grid & Hybrid
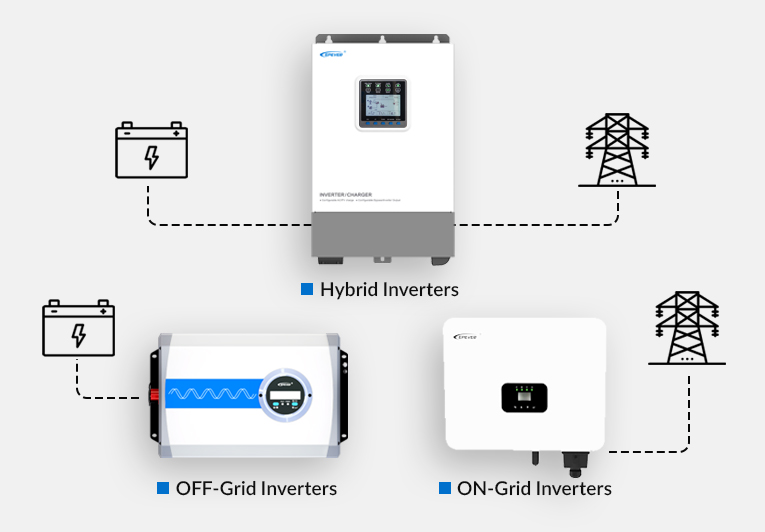
Which Solar Inverter Works for You? On-Grid VS Off-Grid VS Hybrid Inverter
As solar energy adoption grows worldwide, choosing the right inverter becomes critical for maximizing system efficiency and long-term value. Whether you’re powering a city home or a remote cabin, the type of inverter you choose—on-grid or off-grid—determines how you generate, use, and store solar power. In this guide, we break down the key differences between on-grid and off-grid inverters and explore their benefits.
What is an On-Grid Inverter?
How it works
On-grid inverters, also known as grid-tied inverters, are designed to operate with the public electricity grid. These inverters convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is used by most household and commercial appliances. One of the key features of on-grid systems is that they do not require energy storage (batteries). Instead, any excess electricity produced during the day is automatically fed back into the grid. In many regions, this allows system owners to earn credits or monetary compensation through net metering programs.
Additionally, when solar energy production is insufficient—such as during the night or cloudy days—the on-grid system seamlessly draws power from the utility grid to meet energy demand. These systems are typically equipped with safety features to shut down during power outages (anti-islanding), preventing backflow of electricity that could endanger utility workers.
Benefits
- Lower initial investment:On-grid systems do not require batteries, which significantly reduces upfront costs. This makes them ideal for cost-conscious homeowners or businesses wanting to transition to solar energy without large capital expenses.
- Net metering opportunities:In many areas, excess electricity sent to the grid earns credits or payments, helping to offset energy costs and reduce electricity bills over time.
- High energy efficiency:Since energy is used as it is produced, with no need for storage conversion losses, these systems typically achieve higher efficiency compared to battery-based setups.
- Seamless integration:Designed to work directly with existing grid infrastructure, on-grid inverters are easy to integrate and scale.
- Minimal maintenance: Without batteries, the system requires less ongoing maintenance, reducing long-term operating costs.

Ideal use cases
- Urban and suburban homes: In areas with consistent and reliable grid access, on-grid systems can maximize solar usage while keeping costs low.
- Commercial buildings:Businesses can lower operating costs by reducing reliance on grid electricity, especially during peak usage hours.
- Regions with net metering policies:Users can maximize return on investment through credits or incentives for feeding electricity back into the grid.
Installation and Costs
Installing an on-grid inverter is generally simple for residential use. The process involves mounting the unit near the main panel, connecting it to the solar array and the grid, and setting up monitoring.
On-grid systems are also more cost-effective, typically costing 40–50% less than off-grid setups due to the lack of battery storage. However, they can’t supply power during outages, as they shut down automatically for safety.
EPEVER’s on-grid inverters are designed for quick installation and seamless integration with existing electrical systems, minimizing labor costs while maximizing system performance and reliability.
What is an Off-Grid Inverter?
How it works
Off-grid inverters operate independently from the utility grid. They rely on solar panels and batteries to generate and store electricity, providing energy autonomy even in remote areas. DC power from panels is stored in batteries, then converted to AC as needed to power devices. These systems typically include charge controllers to manage battery charging and prevent overcharging or deep discharging.
The process follows these basic steps:
- Solar panels generate DC electricity during daylight hours.
- This electricity passes through a charge controller that manages battery charging.
- The off-grid inverter draws electricity from the batteries, converting DC to AC for household use.
- Excess energy is stored in batteries for use during nights or cloudy days.
Off-grid inverters must handle load changes and battery conditions while delivering stable power.
EPEVER’s models feature advanced battery management and built-in charge controllers, enhancing reliability and energy efficiency—especially in remote installations where consistency is critical.

Benefits
- Complete energy independence:Off-grid systems provide self-sufficiency, allowing users to live or work without relying on external electricity providers.
- Ideal for remote or off-grid areas: In locations where grid access is limited or unavailable, off-grid inverters ensure a consistent power supply.
- Reliable power during outages: Even during grid failures or natural disasters, off-grid systems can provide continuous electricity if solar generation and storage are sufficient.

Ideal use cases
- Remote homes and cabins: In areas where grid connection is impractical or too costly, off-grid systems offer a viable power solution.
- Farms and agricultural setups:Especially useful for powering irrigation systems or equipment in off-grid environments.
- Disaster-prone regions:Off-grid systems ensure that power remains available during emergencies when the grid may be compromised.
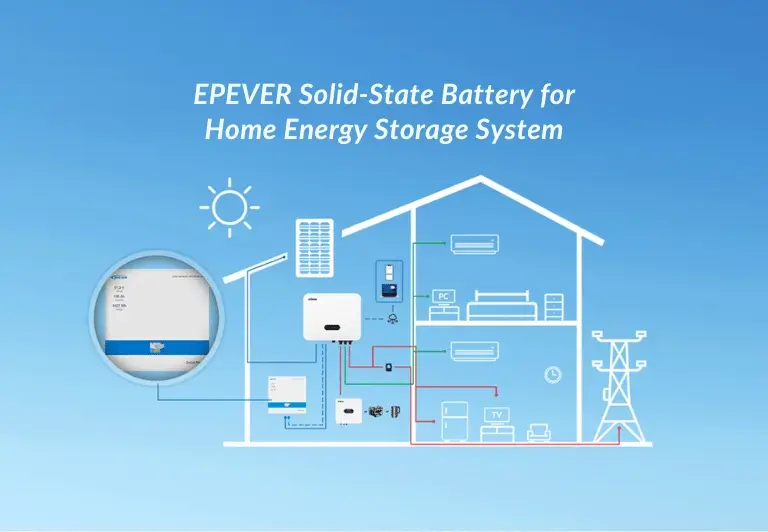
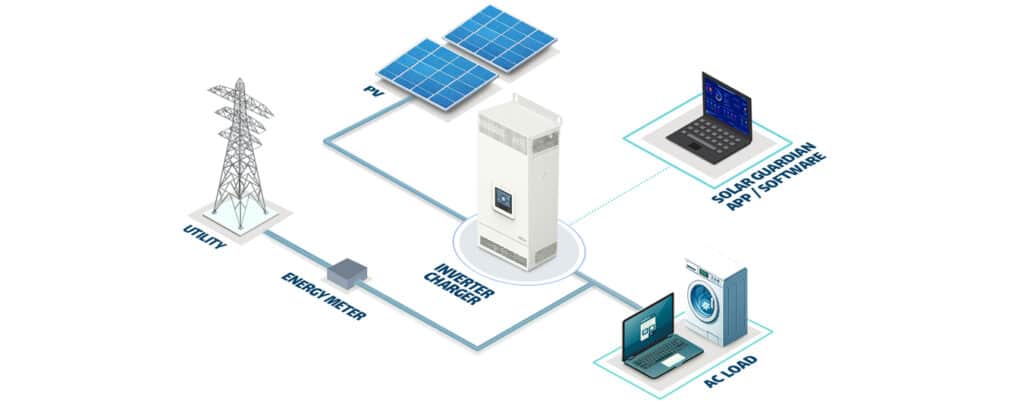
Hybrid Solar Inverters – The Middle Ground
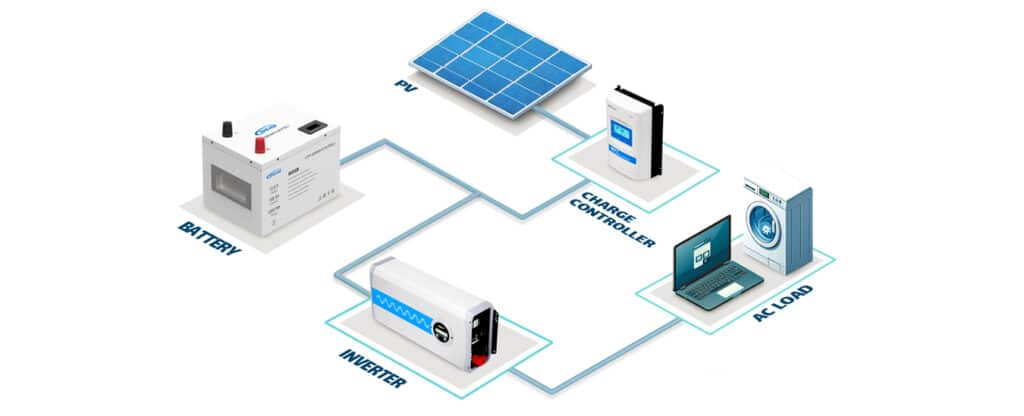
Hybrid inverters combine the key features of both on-grid and off-grid systems, offering flexibility, energy independence, and enhanced control over solar energy usage. These inverters convert DC power from solar panels into AC for immediate use, while also storing surplus energy in batteries for later consumption. During the day, they power loads and charge batteries. At night or during outages, they draw power from batteries. If needed, they can also draw electricity from the grid or feed excess power back into it, depending on system configuration.
Key Characteristics
Bidirectional power flow: Handles energy from solar panels, batteries, and the grid.
Energy optimization: Uses MPPT technology to maximize solar harvest.
Flexibility: Can be installed with or without batteries; allows future upgrades.
Remote monitoring: Many models offer app-based or online tracking for performance and system health.
On-Grid vs Off-Grid vs Hybrid Inverters: Side-by-Side Comparison
Feature | On-Grid Inverter | Off-Grid Inverter | Hybrid Inverter |
Grid Connection | Connected to the public grid | Operates independently | Can connect to both grid and batteries |
Energy Storage | Not required | Requires batteries | Optional—can work with or without batteries |
Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher due to storage needs | Medium—depends on battery configuration |
Use Case | Urban/suburban with grid access | Remote or unreliable grid areas | Areas with grid + need for backup power |
Net Metering | Yes | No | Yes |
Power During Outages | No (shuts down) | Yes (battery backup) | Yes (switches to battery during outages) |
Each inverter type serves a specific role based on location, energy needs, and budget. On-grid systems excel in urban settings with stable grids and net metering. Off-grid inverters shine in remote or independent setups, offering full autonomy. Hybrid inverters provide the best of both worlds, suitable for users who need grid interaction but also desire backup power and flexibility.
- On-grid systems are vulnerable during outages and depend on grid stability.
- Off-grid systems require significant investment in batteries and maintenance.
- Hybrid systems are costlier upfront and require more complex system design.
EPEVER Inverter Solutions – Tailored for Every Scenario
EPEVER offers a comprehensive range of inverters to suit different solar energy setups—from fully off-grid to advanced hybrid systems:
- Pure Sine Wave Off-Grid Inverter(Product: IPT; IP-PLUS; IPB; NP)
A true off-grid solution, designed to operate independently from the grid without battery integration. Ideal for simple setups where direct power conversion from solar panels to appliances is needed. This inverter provides clean, stable AC output for sensitive devices, ensuring energy reliability in remote or mobile environments.
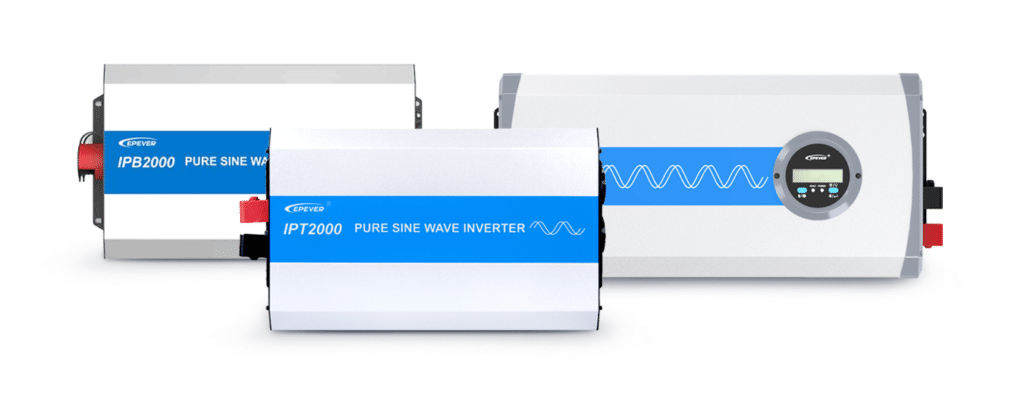

- Off-Grid Hybrid Inverter (Product: UP;HP-AH; UCP; KRP; MP; SIGFI)
Though fundamentally an off-grid inverter, this versatile model features grid input support—allowing it to draw power from the grid when solar and battery resources are insufficient. Commonly known as an off-grid hybrid inverter, it combines solar + battery + optional grid power, ensuring uninterrupted energy supply. Ideal for users in regions with occasional grid access who prioritize solar autonomy but value backup flexibility.
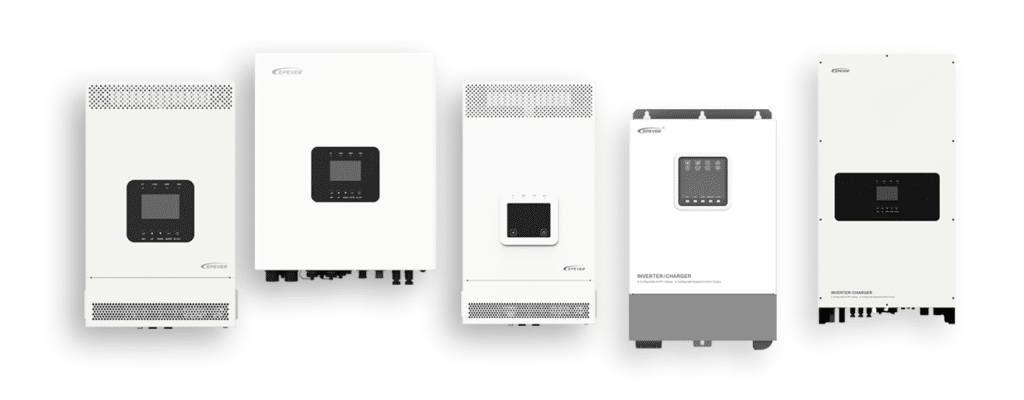
- On-Grid Hybrid Inverter (Product: ELS; EHD)
Designed for typical grid-connected applications, this inverter supplies energy to the grid and to local loads. It also integrates battery storage, allowing surplus solar energy to be stored for later use or fed into the grid for compensation. This on-grid hybrid inverter is perfect for homeowners or businesses seeking net metering benefits while maintaining power during outages.

- On-Grid PV Inverter(SPS, SPT)
A grid-tied inverter solely designed for solar-to-grid applications, with no battery support. It provides efficient solar energy conversion and direct grid feed-in but cannot store energy. Ideal for locations with stable grid access and net metering policies, where users aim to offset electricity bills without investing in battery systems.

Summary of Use Cases:
Pure Off-Grid: Remote areas, mobile applications, minimal load.
Off-Grid Hybrid: Energy independence with occasional grid backup.
On-Grid Hybrid: Grid-tied systems with energy storage + backup.
On-Grid PV: Cost-effective grid feed-in, no storage needed.
With this diverse product lineup, EPEVER ensures that every customer—whether prioritizing autonomy, flexibility, or cost-efficiency—can find a tailored inverter solution that meets their unique energy needs.
How to Choose the Right Inverter for You
Factors to Consider
When determining which inverter type best meets your needs, consider these critical factors:
- Grid reliability: In areas with frequent outages, off-grid or hybrid solutions provide greater energy security.
- Budget constraints: If initial cost is your primary concern, on-grid systems offer the most affordable entry point.
- Energy independence goals: For complete self-sufficiency, only off-grid systems deliver full autonomy.
- Location characteristics: Remote properties often make off-grid systems more economical than extending utility lines.
- Future expandability: Consider how your energy needs might change and which system allows easier scaling.
- Local regulations: Some areas have restrictions or incentives that favor particular system types.
Example: Residential Off-Grid Cabin
Imagine a cabin in a remote area without grid access. Daily energy needs include lights (200W), a fridge (150W), and a water pump (300W), used for about 5 hours daily. Total daily consumption: ~3 kWh. An off-grid system here would require:
Solar panel array producing 4- 5 kWh/day
Battery bank with at least 6 kWh capacity (for autonomy)
Inverter capacity: At least 1kW with 12V/24V support depending on battery configuration.
- For stable grid areas with net metering: On-grid inverter
- For remote locations with unreliable power: Off-grid inverter
- For flexibility and future-proofing: Hybrid inverter
FAQs
Q1: What is the combination of both on-grid and off-grid system called?
A hybrid system. It combines the benefits of grid connection and battery storage.
Q2: Can off-grid inverters work with the grid?
No, off-grid inverters are not designed to connect with the grid. Attempting to do so can be unsafe and non-compliant.
Q3: What is net metering and how does it work?
Answer: Net metering allows solar energy users to send excess electricity back to the grid and receive credits on their utility bills. It helps offset electricity costs and is available in many regions with on-grid systems.
Conclusion
Selecting the right inverter is crucial to achieving a reliable, efficient, and cost-effective solar energy system. On-grid inverters offer simplicity and cost savings for grid-connected users, while off-grid systems provide complete independence in remote or unstable regions. Hybrid inverters blend these capabilities, offering flexibility, backup power, and long-term scalability.
At EPEVER, we offer expert guidance and reliable products tailored to your energy needs. Whether you prioritize the cost-effectiveness of on-grid systems or the independence of off-grid setups, choosing quality components ensures lasting performance. Our inverters meet international standards for safety and efficiency, giving you confidence in every installation. After all, your inverter is the heart of your solar system—choose wisely for long-term, clean energy.